The Functioning Mechanism of Shrinky Dinks
In the realm of childhood nostalgia, few toys can rival the charm of Shrinky Dinks. Originally produced and marketed by K & B Innovations in the 1970s and 1980s, these colourful plastic sheets have long been an indispensable aspect of our current society, not just a fun diversion for artsy kids (and adults), but also a potential tool for serious research.
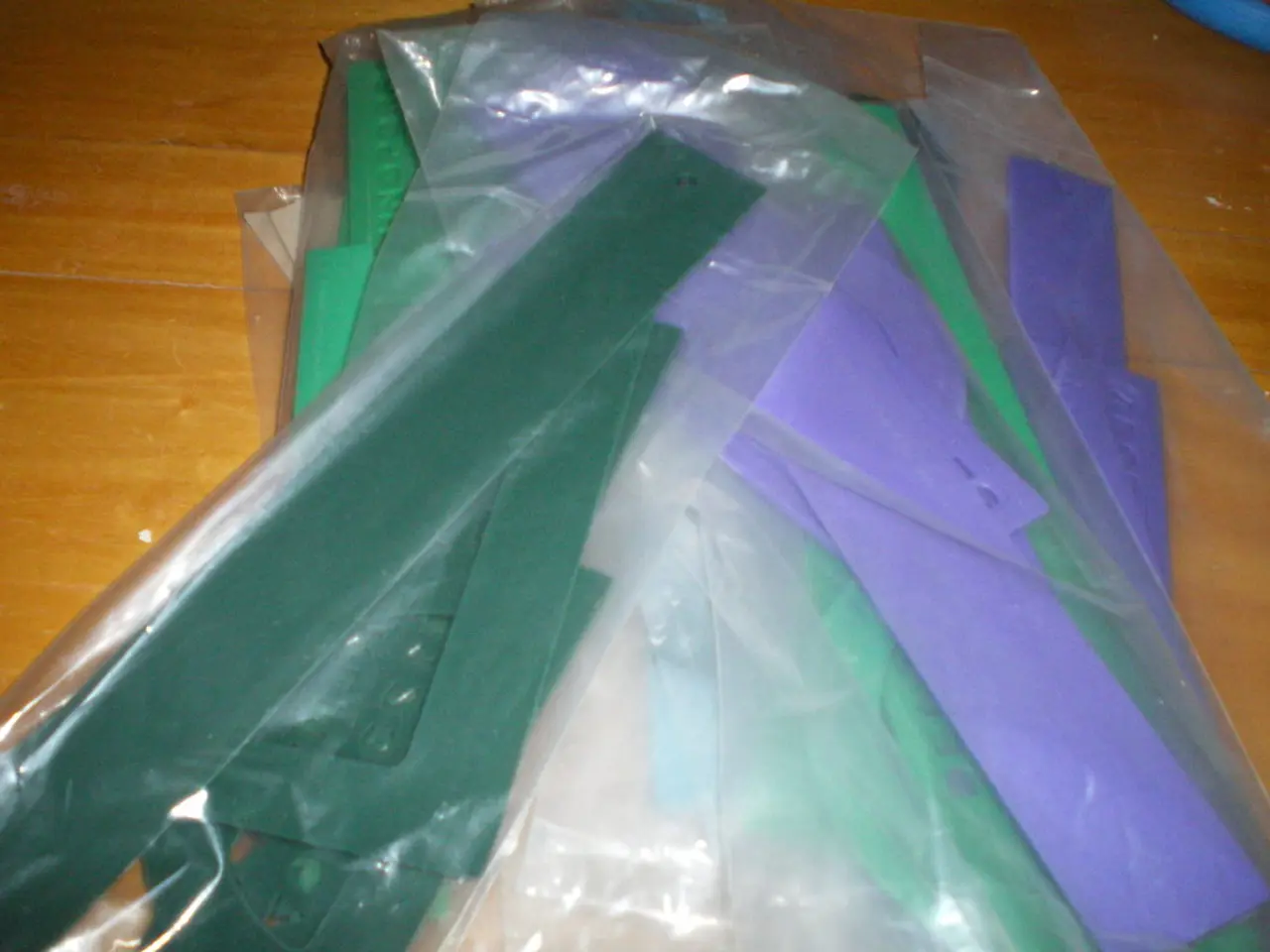
The plastic used in Shrinky Dinks is called polystyrene, a type of polymer that is commonly found in various forms, including the clear lids for sandwiches and other foods in cafeterias. Polystyrene is a long chain of repeating molecules, and its unique properties have made it a valuable resource in numerous industries.
The creation of Shrinky Dinks involves an extrusion process, where manufacturers load all of the ingredients for polystyrene into a heated mixing drum. This pliable, rubbery plastic is then forced through a slot die, creating sheets that are 0.09 inches (2.3 millimeters) thick. At room temperature, these sheets are rigid, lightweight, and transparent. However, when heated in ovens to temperatures above 375 degrees Fahrenheit (190 degrees Celsius), polystyrene melts and can easily be manipulated into many shapes. This is why polystyrene is sometimes referred to as 'memory plastic' because it remembers its original form.
When cooled, the plastic molecules in the sheets 'freeze' into their stretched and flattened form. This is where the magic of Shrinky Dinks truly shines. When shrunk, the sheets of 0.09-inch (2.3-millimeter) plastic are compressed down to 0.01 inches (0.3 millimeters) in thickness. However, to avoid distortion when shrunk, Shrinky Dinks require biaxially oriented polystyrene.
This shrinking effect has caught the attention of researchers, particularly Dr. Michelle Khine, a biomedical engineer at the University of California, Irving. Dr. Khine has utilized the shrinking effects of polystyrene in several projects, creating miniature plumbing for experiments requiring cell assay or very small samples of body fluids. These kinds of devices are used for important purposes such as testing for diseases, determining drug toxicity, and culturing stem cells.
Moreover, polystyrene can be recycled and is often found as recycled plastic No. 6. This eco-friendly aspect of Shrinky Dinks further underscores its potential as a tool for solving some of the world's pressing problems.
In conclusion, Shrinky Dinks, once a beloved toy, is now making a comeback as a valuable resource in scientific research. Its unique properties and potential for recycling make it a promising tool for the future, particularly in any sort of science that relies on small, intricate components.
Read also:
- Crisis in a neighboring nation: immediate cheese withdrawal at Rewe & Co, resulting in two fatalities.
- United Kingdom Christians Voice Opposition to Assisted Dying Legislation
- Democrats are subtly dismantling the Affordable Care Act. Here's the breakdown
- Antisebum skincare products (cream, cleanser, and moisturizer) advocating for self-acceptance and skin confidence.