Avoiding Sleep Errors That Negatively Impact Your Health - Discover and Correct 3 Prevalent Mistakes Tonight
================================================================================
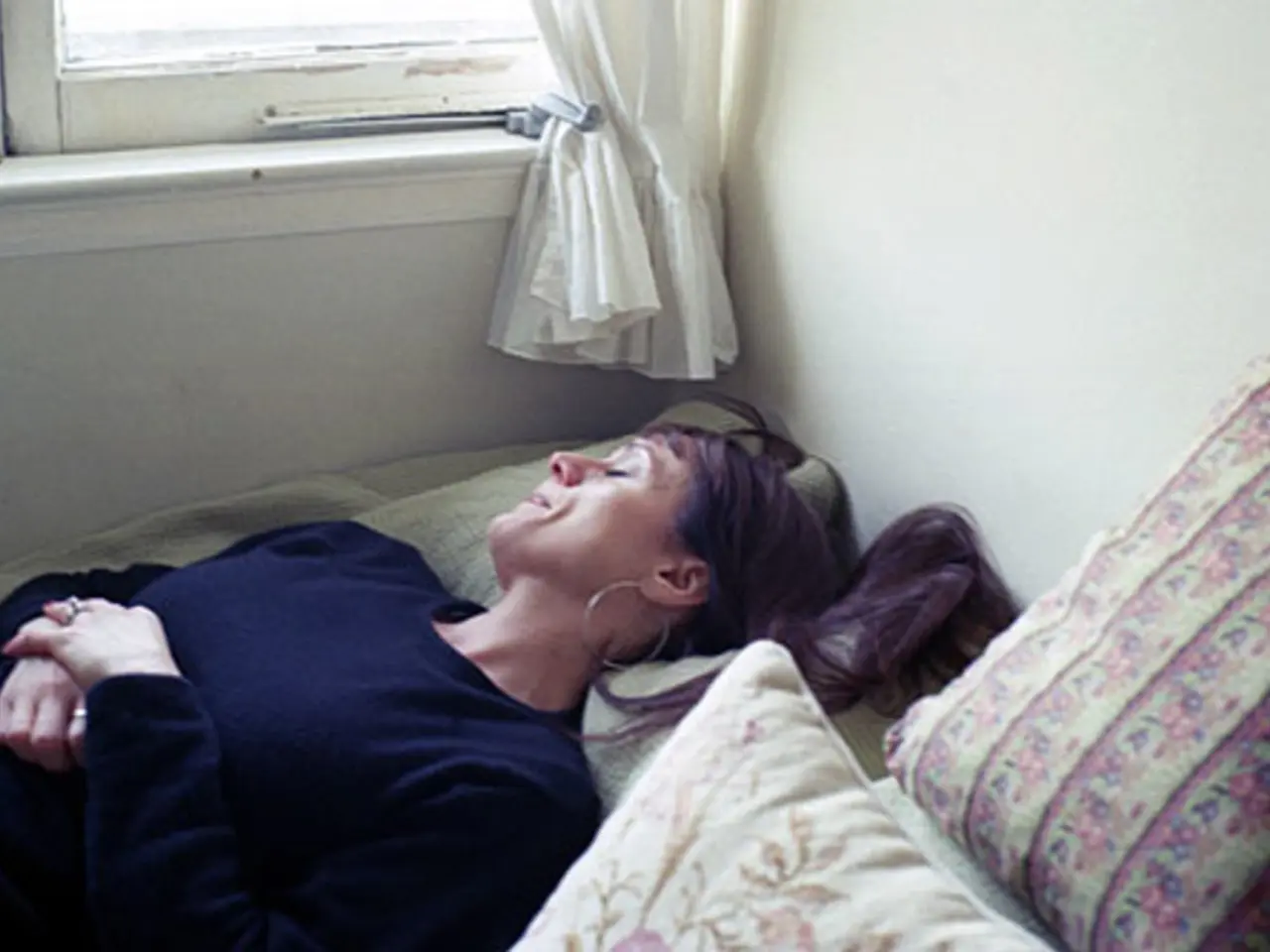
Chronic irregular sleep patterns can have significant negative effects on a person's health. A recent study involving over 80,000 participants has revealed that irregular sleep — defined as going to bed regularly after 12:30 a.m., sleeping less than six hours, or having an inconsistent sleep schedule — is linked to a higher risk of various health problems.
Key Findings
The study, led by Dr. Mark Kovacs, a longevity expert, human performance scientist, and sleep & recovery expert, found that irregular sleep patterns are associated with increased risks for metabolic, cardiovascular, neurological, liver, immune/inflammatory, and mental health outcomes.
In particular, late bedtimes (after 12:30 a.m.) were associated with a 2.57-fold higher risk of liver cirrhosis. Poor interdaily stability (irregular day-to-day timing) was linked to a 2.61-fold higher risk of gangrene and was broadly associated with many other diseases across organ systems.
Short sleep (less than six hours) is associated with increased risks for conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, dementia, Parkinson's disease, and acute kidney failure. The study also found that poor and irregular sleep is tied to higher risks of dementia, depression, and cognitive decline.
Inflammatory pathways and circadian disruption were identified as plausible biological links between irregular sleep and disease development, suggesting systemic effects on metabolism, immune function, and organ health.
Implications for Clinical Practice
The study highlights the importance of sleep regularity in addition to duration. Consistent bedtimes and wake times appear to be important for reducing risk, not just total hours slept. Short, fragmented, or misclassified "long in bed" sleep can be misleading, as some people who report long sleep actually sleep less than six hours, hiding the true risks.
Practical Recommendations
To improve sleep regularity, it is recommended to aim for regular bed and wake times (avoid routinely going to bed after 12:30 a.m.). Targeting sufficient sleep (typically 7–9 hours for most adults) and improving sleep hygiene and circadian cues can also help. Consistent schedule, daytime light exposure, limiting evening light/blue light, and avoiding late stimulants can help stabilize rhythms.
If you have chronic sleep problems or work night/shift schedules, it is advisable to consult a clinician, as there may be targeted interventions (behavioural sleep medicine, circadian therapies) and monitoring to reduce downstream health risks.
In summary, irregular sleep patterns can have profound impacts on a person's health, increasing the risk of various short- and long-term health problems. Regularity, duration, and good sleep hygiene are key factors in maintaining optimal health.
- Science has shown that irregular sleep patterns are linked to an elevated risk of chronic diseases.
- The study emphasizes that sleep regularity is crucial for overall health, beyond just the duration of sleep.
- Late bedtimes may raise the risk of liver cirrhosis by 2.57 times as per the research.
- Inconsistent sleep schedules could increase the risk of gangrene, according to the study's findings.
- Short sleep durations (less than six hours) can enhance the risk of conditions like type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
- Irregular sleep is associated with higher risks of cognitive decline, dementia, and depression.
- Inflammation and circadian disruption might play a role in the development of diseases due to irregular sleep.
- The research emphasizes the importance of prioritizing sleep regularity for better health outcomes.
- Adhering to regular bedtimes and wake times may help reduce the risk of various health problems.10.Fragmented or misclassified sleep could hide the true risks, as some individuals who claim to sleep long hours may actually be sleeping less than the recommended amount.
- Sufficient sleep, improved sleep hygiene, and circadian cues are essential for maintaining good health.
- Consistency in schedule, daytime light exposure, and avoiding late stimulants can assist in stabilizing rhythms.
- For those experiencing chronic sleep issues, consulting a clinician may be helpful in identifying targeted interventions and monitoring.
- Circadian therapies could be useful in mitigating the health risks associated with irregular sleep.
- Education in self-development is necessary for learning about the importance of sleep regularity for health and wellness.
- Prioritizing personal growth includes understanding the role of sleep regularity in maintaining good health.
- Career development may require individuals to put a conscious effort into establishing sleep regularity.
- Fitness and exercise routines can benefit from maintaining consistent sleep patterns.
- Irregular sleep patterns can impact performance in sports, such as football, NBA, WNBA, baseball, hockey, golf, tennis, and mixed martial arts.
- Sports betting may be affected by the impact of irregular sleep on athletes’ performances.
- The consequences of irregular sleep in racing sports such as American football, NASCAR, F1 Grand Prix, horse racing, and NCAAC football can compromise athletes' performance and overall health.